This quick tutorial is going to show you how to get your Linux system information in terminal with a command line utility called screenfetch.
Screenfetch can display the following information:
- the name of your distro
- Linux kernel version
- uptime
- the number of installed packages on your system
- shell name and version
- screen resolution
- the name and version of your desktop environment
- window manager
- theme, font
- CPU, GPU and RAM info
First let’s see how to install screenfetch on Linux. Screenfetch is available in most Linux distribution repositories.
Install Screenfetch on Your Linux Distro
Debian 8, Ubuntu 16.04/16.10, Linux Mint 18, Elementary OS Loki
Open up a terminal window and run the following command:
sudo apt install screenfetch
If you want to get the latest version as soon as possible, then install screenfetch from PPA.
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:djcj/screenfetch sudo apt update sudo apt install screenfetch
Install Screenfetch on Fedora, Korara
sudo dnf install screenfetch
Install Screenfetch on Arch Linux, Manjaro, Apricity OS
sudo pacman -S screenfetch
Using Screenfetch to Get Linux System Information
It’s very easy. Simply run the following command in terminal:
screenfetch
You will see an ASCII logo and various information.
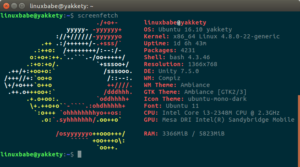
How to Automatically Display System Information
If you want to display these info upon launching your terminal without having to manually run screenfetch command, then all you need to do is to add the command in your .bashrc script.
Edit .bashrc script with a command line text editor such as nano.
nano ~/.bashrc
Add screenfetch command at the bottom of the file like below.
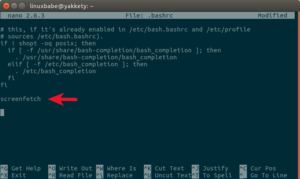
In nano text editor, press CTRL+O to save the file, then press CTRL+X to exit. Close your terminal and re-open it. You should see your Linux system information without manually typing screenfetch command.